Navigating the world of dairy-free alternatives can be both an adventure and a puzzle, especially when following the GAPS (Gut and Psychology Syndrome) protocol. Designed to heal the gut and support mental health, GAPS often requires eliminating traditional dairy, pushing individuals to explore a variety of substitutes. Whether driven by necessity or curiosity, choosing the right dairy-free options becomes a crucial step in maintaining the diet’s integrity while ensuring nutritional balance. In this article, we’ll delve into the best practices for selecting dairy-free alternatives that align with GAPS principles, helping you make informed choices with confidence and ease.
Table of Contents
- Exploring Dairy-Free Options Compatible with the GAPS Diet
- Nutritional Benefits and Potential Challenges of Dairy Alternatives
- Selecting High-Quality Dairy Substitutes for Optimal Gut Health
- Incorporating Homemade Dairy-Free Recipes into Your GAPS Meal Plan
- Tips for Reading Labels and Avoiding Hidden Ingredients on the GAPS Diet
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
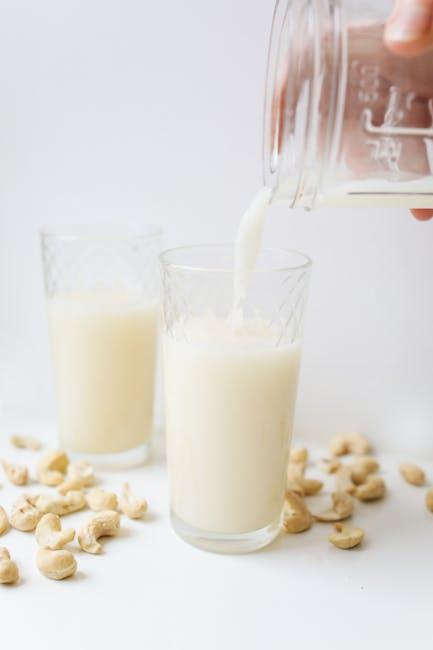

Exploring Dairy-Free Options Compatible with the GAPS Diet
When navigating the world of dairy-free alternatives on the GAPS diet, it’s essential to focus on options that align with the diet’s emphasis on gut healing and nutrient density. Many commercially available substitutes may contain additives or sugars that could interfere with your progress. Opt for simple, minimally processed foods like homemade nut milks (almond, macadamia), coconut milk, or ghee, which is clarified butter free from milk solids and generally tolerated in later GAPS stages. Incorporating cultured dairy-free products like coconut yogurt can also be beneficial, as they provide probiotics while keeping your gut flora balanced.
To make shopping easier and more aligned with GAPS principles, keep an eye out for the following characteristics in dairy-free products:
- No additives or preservatives, especially carrageenan and gums.
- Unrefined ingredients, avoiding refined sugars and oils.
- Organic options, reducing exposure to pesticides.
- High fat content, supporting gut repair and energy.
| Alternative | Best For | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Homemade Almond Milk | Versatile drinking and cooking | Use raw, soaked almonds for easier digestion |
| Ghee | Cooking and fat source | Clarified, lactose-free butter |
| Coconut Yogurt | Probiotic-rich snack | Choose unsweetened and organic |
| Cashew Cream | Thickener and base for sauces | Blend soaked raw cashews |
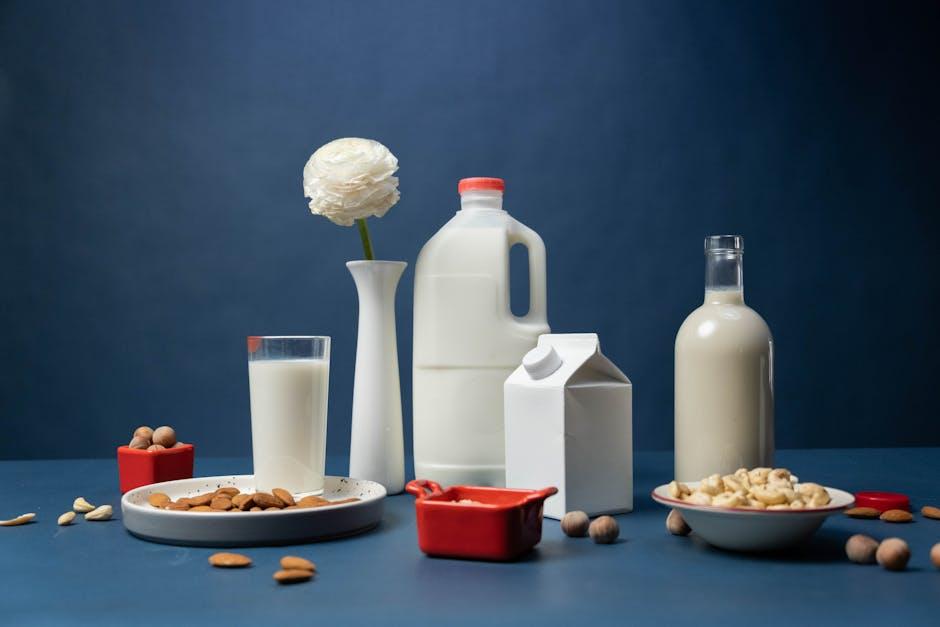

Nutritional Benefits and Potential Challenges of Dairy Alternatives
Dairy alternatives offer a variety of nutritional profiles that can be beneficial for those following the GAPS (Gut and Psychology Syndrome) protocol. Many of these substitutes—such as almond, coconut, and hemp milk—are rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals that support gut health and overall well-being. For example, coconut milk is a natural source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which may aid digestion and provide quick energy. Additionally, some plant-based milks are fortified with calcium and vitamin D, helping bridge potential nutrient gaps. Incorporating these alternatives can diversify your diet, especially when aiming to reduce inflammation and nurture gut flora.
However, choosing dairy-free options requires careful consideration to avoid hidden pitfalls that might disrupt GAPS healing. Many commercial varieties contain additives like carrageenan, gums, and sugars that can irritate the gut lining or provoke sensitivities. Those with nut allergies or intolerances must beware of products made from common allergens such as almonds or cashews. It’s crucial to scrutinize labels for unwanted ingredients and prefer unsweetened, minimally processed products. Below is a quick comparison of popular dairy-free options, highlighting their nutritional strengths and potential challenges:
| Dairy Alternative | Key Nutrients | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Coconut Milk | MCTs, Iron, Potassium | Added thickeners, high in saturated fat |
| Almond Milk | Vitamin E, Calcium (fortified) | Nut allergens, often diluted |
| Hemp Milk | Omega-3 & 6 fatty acids, Magnesium | Less common, may have additives |
| Oat Milk | Fiber, Iron, B vitamins (fortified) | Higher glycemic load, gluten exposure risk |

Selecting High-Quality Dairy Substitutes for Optimal Gut Health
When choosing dairy-free alternatives that support a sensitive gut, focusing on ingredients and production methods can make all the difference. Prioritize options made from whole-food sources, such as almond, coconut, or oat bases that contain minimal additives and preservatives. Fermented dairy substitutes, like coconut yogurt with live cultures, can further enhance digestion by promoting beneficial gut bacteria. Always check labels for hidden sugars, gums, or artificial thickeners that might trigger inflammation or digestive discomfort. Selecting products rich in natural probiotics and enzymes can offer an added layer of gut-friendly benefits.
Understanding how certain components affect gut health will guide smarter shopping choices. For instance, while many opt for plant-based milks, not all are equally nourishing or gut-compatible. Here’s a quick reference table outlining common dairy substitutes and their gut health profiles:
| Substitute | Gut Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Coconut Milk | Rich in MCTs aiding digestion | May be high in saturated fat |
| Almond Milk | Low in carbs, gentle on gut | Watch for added sugars |
| Oat Milk | Good source of fiber | May aggravate gluten-sensitive individuals |

Incorporating Homemade Dairy-Free Recipes into Your GAPS Meal Plan
Integrating homemade dairy-free recipes into your GAPS meal plan is a wonderful way to ensure both nutritional balance and flavor diversity. Crafting meals at home means you control the quality and freshness of ingredients, allowing you to avoid unwanted additives commonly found in store-bought alternatives. Focus on using nutrient-dense whole foods like coconut milk, almond cream, and homemade nut cheeses to replace traditional dairy. These ingredients not only enrich your meals but also complement the GAPS diet’s emphasis on healing and gut restoration.
To make the transition smoother, consider experimenting with various homemade dairy-free staples that align with GAPS principles. Here are some popular choices to get you started:
- Coconut yogurt — creamy, probiotic-rich, and easy to prepare using just coconut milk and a starter culture.
- Almond milk — a versatile base for soups and smoothies, made by blending soaked almonds with water.
- Cashew cheese — a soft, tangy spread perfect for snacking or topping, made from soaked cashews and nutritional yeast.
| DIY Dairy-Free Item | Key Ingredients | Benefits for GAPS |
|---|---|---|
| Coconut Cream | Coconut milk, agar-agar | Rich in healthy fats, supports digestion |
| Cashew Sour Cream | Cashews, lemon juice, probiotic culture | Promotes gut flora, creamy texture |
| Almond Milk | Almonds, filtered water, pinch of salt | Low allergy risk, versatile in recipes |

Tips for Reading Labels and Avoiding Hidden Ingredients on the GAPS Diet
When selecting dairy-free alternatives for the GAPS diet, the devil is often in the details. Labels can be a maze of confusing terms, so it’s essential to look beyond just the front packaging. Focus on the ingredient list, and be suspicious of any item you don’t recognize or that sounds overly processed. Common hidden ingredients that might sneak into dairy-free products include starches, gums, preservatives, and sweeteners—all of which can conflict with GAPS principles. Watch for words like To make label-reading easier, keep a handy checklist of approved and banned ingredients next to you while shopping. Here’s a quick reference table to help identify ingredients often hidden in dairy-free options: Q&A: Buying Dairy-Free Alternatives for GAPS Q1: What is the GAPS diet, and why might someone seek dairy-free alternatives while following it? Q2: Are all dairy-free alternatives suitable for someone on the GAPS diet? Q3: What are some good dairy-free alternatives compatible with the GAPS diet? Q4: How can I prepare my own dairy-free fermented foods for the GAPS diet? Q5: Can I rely solely on dairy-free alternatives while on GAPS, or should I try reintroducing dairy later? Q6: Where should I shop for GAPS-friendly dairy-free products? Q7: What is the biggest challenge when buying dairy-free alternatives on the GAPS diet? This Q&A aims to guide readers thoughtfully through the nuances of incorporating dairy-free alternatives into the GAPS diet, balancing healing goals with practical choices. Navigating the world of dairy-free alternatives for the GAPS diet can feel like a culinary adventure—one that requires curiosity, patience, and a bit of experimentation. While traditional dairy plays a significant role in many diets, embracing thoughtful substitutes opens the door to nourishing your body without compromise. By choosing quality products and listening to your body’s responses, you can craft a diet that supports your healing journey while delighting your palate. Ultimately, the path to wellness is as unique as you are—so keep exploring, stay informed, and savor every step along the way.
Hidden Ingredient
Common Source
GAPS Friendly?
Modified Starch
Corn, Potato
No
Maltodextrin
Rice, Corn Sugar
No
Natural Flavors
Various
Uncertain
Guar Gum
Plant Extract
Use with Caution
Xanthan Gum
Bacterial Fermentation
Use with Caution
Q&A
A1: The GAPS (Gut and Psychology Syndrome) diet is designed to help heal the gut lining and improve mental and physical health by eliminating certain foods and focusing on nutrient-dense, easily digestible options. While traditional GAPS emphasizes homemade fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir, some individuals may be dairy-sensitive or allergic, prompting them to seek dairy-free alternatives that align with the diet’s principles.
A2: Not necessarily. Many commercial dairy-free products—such as store-bought soy, almond, or oat milks—contain additives, thickeners, or sugars that are not compatible with the GAPS healing process. It’s essential to look for clean, minimally processed options without unnecessary fillers or sweeteners to stay true to GAPS guidelines.
A3: Bone broth, homemade nut milks (soaked and strained), and well-prepared fermented coconut products are often well-tolerated. Homemade versions are preferred since you can control the ingredients and fermentation processes, ensuring they contribute to gut healing rather than hindering it.
A4: Start with raw coconut milk or soaked cashews as a base, then introduce probiotic cultures to ferment them. This creates nourishing, gut-friendly foods similar to traditional fermented dairy but without lactose or casein. Recipes and starter cultures are available in many GAPS resources, emphasizing patience and careful monitoring for tolerance.
A5: Many GAPS followers aim to reintroduce well-tolerated fermented dairy as healing progresses because of its nutrient density and probiotic benefits. However, for those with persistent allergies or intolerances, dairy-free alternatives provide a valuable option to maintain nutrition without sacrificing gut health.
A6: Farmer’s markets, health food stores, and specialty online retailers often carry organic, additive-free ingredients suitable for homemade preparations. Reading labels carefully and choosing whole, natural foods is crucial when shopping for dairy-free options on GAPS.
A7: The main hurdle is finding products free from preservatives, stabilizers, and sugars that can disrupt the delicate gut healing process. Homemade preparations demand more time and effort but offer greater control, making the extra work worthwhile for those committed to the diet’s success.
Final Thoughts











Leave feedback about this