In the bustling world of health and wellness, digestive enzymes have quietly gained a spotlight—heralded by some as the secret to smoother digestion, and dismissed by others as just another wellness fad. But what exactly are these biological catalysts, and do you truly need to invite them to your dinner table? Whether you’re curious about boosting nutrient absorption, calming an occasionally upset stomach, or simply intrigued by the science behind digestion, understanding the role of digestive enzymes might reveal answers you didn’t know you were searching for. Let’s embark on a journey through the digestive tract to explore whether supplemental enzymes deserve a place in your daily regimen—or if your body’s own chemistry is already doing the job just fine.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Digestive Enzymes and Their Role in Digestion
- Signs You Might Benefit from Digestive Enzyme Supplements
- Natural Sources of Digestive Enzymes to Include in Your Diet
- Evaluating the Safety and Effectiveness of Enzyme Supplements
- Guidelines for Choosing the Right Digestive Enzyme Product for You
- Q&A
- In Summary

Understanding Digestive Enzymes and Their Role in Digestion
Digestive enzymes are specialized proteins that act as catalysts in breaking down the food we consume into smaller, absorbable components. These enzymes target specific macronutrients:
- Proteases break down proteins into amino acids.
- Amylases convert carbohydrates into simple sugars.
- Lipases digest fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Produced primarily by the pancreas, stomach, and small intestine, these enzymes streamline the digestive process, ensuring vital nutrients can be absorbed efficiently. When enzyme production is inadequate, food remains partially digested, which can lead to bloating, discomfort, or nutrient deficiencies.
| Enzyme | Macronutrient Target | Primary Source |
|---|---|---|
| Pepsin | Protein | Stomach |
| Amylase | Carbohydrates | Pancreas & Saliva |
| Lipase | Fat | Pancreas |
Understanding how these enzymes function highlights their crucial role in maintaining digestive health and overall well-being. Aside from natural enzyme production, certain factors can influence enzyme activity, such as age, dietary habits, or medical conditions. Incorporating enzyme-rich foods or supplements may support digestion when natural enzyme output declines.

Signs You Might Benefit from Digestive Enzyme Supplements
If you frequently experience discomfort after meals, it might be your body’s way of telling you that it needs a little extra help breaking down food. Common signs include persistent bloating, uncomfortable gas, or irregular bowel movements. When your digestive system struggles to fully process the nutrients from your diet, it can lead to a feeling of heaviness or sluggishness. Noticing food intolerances that don’t align with allergies could also point towards enzyme insufficiency.
Other indicators to watch for are:
- Unexplained fatigue after eating
- Frequent heartburn or acid reflux
- Craving for sweets or starchy foods
- Skin issues or irritations linked to diet
While these signs don’t automatically mean you need supplements, they do suggest that digestive enzyme support could enhance your nutrient absorption and overall wellness. To give you a clearer picture, this table summarizes potential symptoms and what they might indicate:
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Benefit of Enzyme Support |
|---|---|---|
| Bloating & Gas | Incomplete carb digestion | Improved carbohydrate breakdown |
| Fatigue After Eating | Poor protein digestion | Enhanced protein absorption |
| Heartburn | Acid imbalance | Better food breakdown & less reflux |
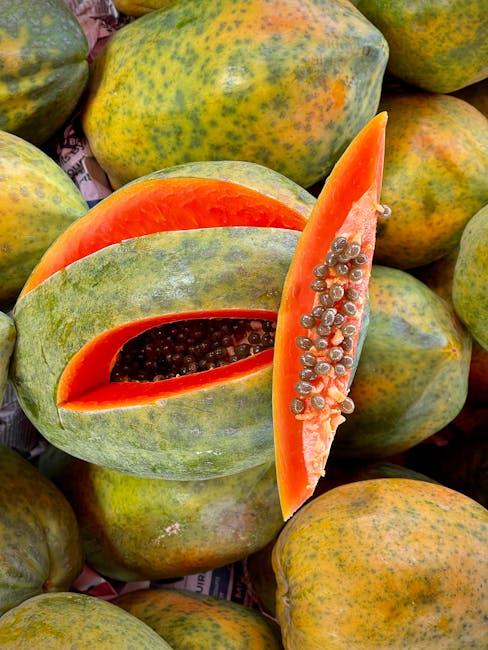

Natural Sources of Digestive Enzymes to Include in Your Diet
Incorporating foods rich in natural digestive enzymes can significantly improve your body’s ability to break down nutrients and enhance overall gut health. These enzymes, found abundantly in certain fruits and fermented foods, work to pre-digest compounds even before they reach your stomach. For instance, pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme known to help break down proteins, while papaya boasts papain, another potent protein-digesting enzyme. Including these fruits in your diet not only adds vibrant flavors but also supports efficient digestion naturally.
Beyond fruits, several other ingredients serve as great sources of digestive enzymes and can be easily integrated into meals:
- Kimchi and sauerkraut – fermented vegetables rich in lactase and other digestive enzymes
- Ginger – stimulates the production of digestive juices
- Mango – contains amylase, which aids in carbohydrate breakdown
- Honey – naturally contains enzymes that assist digestion
| Food | Key Enzyme | Digestive Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pineapple | Bromelain | Protein digestion |
| Papaya | Papain | Protein breakdown |
| Mango | Amylase | Carbohydrate breakdown |
| Kimchi | Lactase | Lactose digestion |

Evaluating the Safety and Effectiveness of Enzyme Supplements
When considering enzyme supplements, it’s essential to weigh their safety and efficacy carefully. Clinical research indicates that many enzyme formulations are well-tolerated by the majority of users, with minimal adverse effects reported. However, individual responses can vary due to factors such as underlying health conditions, existing medications, and product quality. Always look for supplements that have undergone rigorous third-party testing and contain clear labeling of enzyme types and concentrations.
Effectiveness largely depends on the specific digestive challenges being addressed. Enzyme supplements may support digestion by:
- Enhancing nutrient breakdown in cases of enzyme insufficiency
- Alleviating symptoms such as bloating and indigestion
- Supporting optimal digestion for various macronutrients, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
Before starting any regimen, consulting a healthcare professional can ensure that enzyme supplementation is appropriate and safe for your individual needs.
| Aspect | Safety | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Adverse Effects | Mild GI discomfort | Varies by enzyme type |
| Quality Indicators | Third-party testing | Standardized enzyme units |
| Target Use | Generally safe for most adults | Specific enzyme deficiency |

Guidelines for Choosing the Right Digestive Enzyme Product for You
Before selecting a digestive enzyme supplement, it’s crucial to identify your specific digestive needs. Consider which macronutrients—proteins, fats, or carbohydrates—your body struggles to break down. Look for a product that lists enzymes targeting these areas, such as protease for proteins, lipase for fats, and amylase for carbohydrates. Additionally, consider any food sensitivities or conditions like lactose intolerance, as enzymes like lactase can be game-changers. Checking product labels for potency, purity, and allergen information ensures you’re making a safe and effective choice.
Price and form factor also play a vital role in your decision. Digestive enzymes come in various forms—capsules, tablets, powders, or even chewables—so choose one that fits seamlessly into your daily routine. Below is a quick comparison to help simplify your choice:
| Form | Best For | Convenience | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsules | Precise dosing | Easy to swallow | Moderate |
| Powders | Customizable dosing | Mix with food or drink | Affordable |
| Chewables | Quick absorption | Travel-friendly | Higher |
Ultimately, selecting a digestive enzyme supplement is about matching the product’s strengths with your lifestyle and digestive profile, helping maximize the benefits they can provide.
Q&A
Q&A: Digestive Enzymes – Do You Need Them?
Q1: What exactly are digestive enzymes?
A1: Digestive enzymes are natural proteins produced by your body that help break down food into smaller molecules so your body can absorb nutrients effectively. Think of them as tiny scissors that cut through proteins, fats, and carbohydrates to make digestion smoother.
Q2: Where are digestive enzymes produced in the body?
A2: Your body primarily produces digestive enzymes in the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. Each location releases specific enzymes targeting different types of food molecules.
Q3: Why might someone consider taking digestive enzyme supplements?
A3: Some people experience digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, or indigestion, which can indicate their body isn’t producing enough enzymes. Supplements may help ease these symptoms by improving digestion and nutrient absorption.
Q4: Who might benefit most from digestive enzyme supplements?
A4: People with certain health conditions like pancreatic insufficiency, lactose intolerance, or gluten sensitivity may benefit. Additionally, older adults or those with digestive disorders might find enzyme supplements helpful, but it’s best to consult a healthcare provider.
Q5: Are digestive enzyme supplements safe for everyone?
A5: Generally, they are considered safe when taken as directed, but some individuals could experience allergic reactions or interact with other medications. It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare professional before starting any supplement.
Q6: Can digestive enzymes help with weight loss or detoxification?
A6: While they can support digestion, digestive enzymes are not magic pills for weight loss or detox. Their primary role is to aid nutrient absorption, and they should be part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Q7: How can you naturally support your body’s digestive enzyme production?
A7: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods like yogurt, avoiding overeating, managing stress, and staying hydrated can all boost your body’s natural enzyme activity.
Q8: Should everyone take digestive enzymes just in case?
A8: Not necessarily. For most people with healthy digestion, the body produces sufficient enzymes on its own. Supplements are typically reserved for those showing specific digestive issues or diagnosed enzyme deficiencies.
Q9: How do you know if your digestive enzymes are low?
A9: Persistent digestive symptoms such as bloating, frequent gas, undigested food in stool, or nutrient deficiencies might suggest low enzyme activity. Medical testing can confirm this.
Q10: What’s the bottom line on digestive enzymes?
A10: Digestive enzymes play a vital role in breaking down food, and while supplements can help those with certain conditions, most people don’t need them. Focus on a healthy diet and lifestyle first, and consult a healthcare provider if digestive troubles persist.
In Summary
In the intricate dance of digestion, enzymes play a silent yet vital role, breaking down the foods we enjoy into the nutrients our bodies crave. While most people produce enough of these biological catalysts naturally, certain conditions or dietary habits may call for a little extra support. Whether through supplements or mindful eating, understanding digestive enzymes empowers you to make choices that best suit your body’s unique rhythm. Ultimately, the question isn’t just do you need them? but rather how can you listen to your gut and nurture its delicate balance?












Leave feedback about this