In a world where chronic pain has become an all-too-familiar companion for many, the quest for relief often feels endless. Amidst the myriad of treatments, diets, and remedies, one approach has been quietly gaining attention for its promise to transform lives—both physically and mentally. The GAPS (Gut and Psychology Syndrome) diet, originally designed to heal the gut, is now inspiring those burdened by persistent pain to reconsider the root causes of their discomfort. This article explores how embracing the GAPS diet can unlock a path to living pain-free, shedding light on the powerful connection between gut health and overall well-being.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Core Principles Behind the GAPS Diet
- How Gut Health Influences Chronic Pain and Inflammation
- Incorporating Fermented Foods for Natural Healing
- Practical Meal Planning Tips to Maximize GAPS Benefits
- Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Diet for Long-Term Relief
- Q&A
- To Wrap It Up

Understanding the Core Principles Behind the GAPS Diet
The GAPS Diet revolves around nurturing the digestive system by eliminating toxins and irritants while promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Central to this approach is the belief that a healthy gut lining can significantly reduce inflammation and alleviate chronic pain. The diet emphasizes nutrient-dense, easily digestible foods such as homemade broths, fermented vegetables, and high-quality animal fats, which work synergistically to restore gut flora balance and enhance overall digestion. This holistic focus on gut health not only supports physical well-being but also improves mental clarity and energy levels.
At its core, the GAPS protocol incorporates specific practices designed to support healing and maintain long-term gut integrity:
- Elimination of sugars and processed foods: Removing these reduces harmful bacteria and yeast overgrowth.
- Consumption of fermented foods: Enhances probiotic populations for better digestion and immune function.
- Inclusion of homemade bone broths: Rich in collagen and gelatin to repair intestinal lining.
- Gradual reintroduction of foods: Helps identify sensitivities while ensuring gut adaptation.
| Principle | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Gut wall repair | Reduces permeability and inflammation |
| Microbiome balance | Strengthens immunity and digestion |
| Anti-inflammatory foods | Lessens chronic pain and discomfort |
| Detoxification | Removes toxins burdening the body |

How Gut Health Influences Chronic Pain and Inflammation
Emerging research reveals that the state of our gut plays a pivotal role in modulating chronic pain and inflammation throughout the body. A compromised gut lining can allow harmful substances to leak into the bloodstream, triggering widespread immune responses and amplifying pain signals. This connection highlights the importance of nurturing a balanced microbiome—not just for digestion but as a foundational element of holistic pain management. Through targeted dietary strategies, such as the GAPS diet, it becomes possible to restore gut integrity, calm inflammatory pathways, and ultimately reduce the burden of persistent pain.
Key mechanisms linking gut health and chronic pain include:
- Disruption of tight junctions causing “leaky gut” and immune activation
- Imbalance of gut bacteria affecting inflammatory cytokine production
- Altered neurotransmitter regulation influencing pain perception
- Reduced nutrient absorption impairing tissue repair and recovery
| Gut Factor | Impact on Pain & Inflammation |
|---|---|
| Leaky Gut | Systemic inflammation and sensitized pain nerves |
| Dysbiosis | Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines |
| Low Short-Chain Fatty Acids | Weakened anti-inflammatory signaling |
| Malabsorption | Deficiency in healing nutrients like Zinc & Omega-3s |
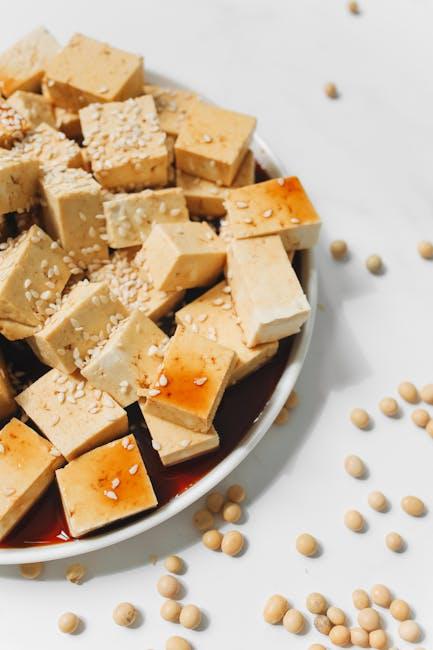

Incorporating Fermented Foods for Natural Healing
Fermented foods serve as a cornerstone in the natural healing journey inspired by the GAPS diet, offering a rich source of probiotics to restore gut health and reduce inflammation. These living foods, such as sauerkraut, kefir, and kimchi, work to rebalance the microbiome by introducing beneficial bacteria that support digestion and strengthen the immune system. Consuming them regularly can help alleviate chronic pain by calming the gut-brain axis and enhancing nutrient absorption, allowing the body to heal from within.
- Sauerkraut: Packed with fiber and enzymes for gut repair
- Kefir: Rich in diverse probiotics to boost immunity
- Kimchi: Offers antioxidants that combat oxidative stress
- Fermented bone broth: Provides collagen and minerals to rebuild tissues
The transformative power of these fermented staples is often underestimated. To emphasize their benefits, consider the following table summarizing key effects of popular fermented foods incorporated in the GAPS diet:
| Fermented Food | Main Benefit | Healing Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| Sauerkraut | Fiber-rich | Improves digestion and reduces bloating |
| Kefir | Probiotic-rich | Enhances immune response |
| Kimchi | Antioxidant-packed | Reduces inflammation and oxidative damage |
| Fermented Bone Broth | Collagen source | Supports joint and tissue repair |

Practical Meal Planning Tips to Maximize GAPS Benefits
To effectively harness the full potential of the GAPS diet, incorporating consistent meal prep routines can be a game-changer. Setting aside a couple of hours each week to prepare core ingredients—such as homemade bone broth, fermented vegetables, and slow-cooked meats—sets a solid foundation for your daily meals. This approach minimizes stress around food choices and ensures that nutrient-dense, gut-healing options are always on hand. Remember, variety within the approved foods not only keeps your palate engaged but also supplies a broader spectrum of essential nutrients.
In addition to pre-planning, consider organizing your shopping list into specific GAPS-friendly categories. This reduces overwhelm at the grocery store and facilitates balanced meal assembly at home. Here are some handy groupings for your list:
- Proteins: cold-pressed organic meats, free-range eggs, wild-caught fish
- Vegetables: leafy greens, fermented cucumbers, squash varieties
- Fats: grass-fed butter, coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil
- Fermented Foods: homemade sauerkraut, kefir, natural yogurt
| Meal Component | Example Foods | Preparation Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Broths & Soups | Chicken bone broth, vegetable broth | Cook in bulk; freeze in portions |
| Main Proteins | Slow-roasted meats, steamed fish | Use slow cooker or oven for ease |
| Vegetables | Steamed greens, fermented veggies | Batch-ferment and steam fresh daily |

Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Diet for Long-Term Relief
Tracking your progress is essential to harnessing the full benefits of the GAPS diet and ensuring lasting relief from pain. Keep a detailed journal documenting daily meals, symptoms, energy levels, and emotional wellbeing. This practice helps to identify food triggers or deficiencies and highlights which diet phases are most effective. Using simple tools like habit-tracking apps or spreadsheets can enhance your awareness and motivate consistency. Pay close attention to subtle changes in digestion, sleep, and mood; these often reveal valuable insights before more obvious improvements appear.
Flexibility is key as your body adapts over time. Gradual reintroduction of new foods or adjustments in portion sizes should be guided by your observations and, if possible, by consulting with a nutritionist familiar with GAPS. Consider scheduling monthly reviews where you assess symptoms alongside dietary choices and tweak elements such as:
- Fermented foods to support gut flora balance
- Bone broth consumption for its healing properties
- Sugar and starch intake moderation to minimize inflammation
- Herbal supplements for targeted relief
| Month | Key Focus | Symptoms to Monitor |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | Strict elimination and gut healing | Digestive discomfort, energy dips |
| 3-4 | Reintroduction of tolerated foods | Inflammation, joint pain |
| 5+ | Long-term maintenance and variety | Overall pain levels, mental clarity |
By staying vigilant and adaptable, you empower yourself to craft a personalized diet that promotes sustained wellness and a pain-free life.
Q&A
Q&A: Living Pain-Free Thanks to the GAPS Diet
Q1: What is the GAPS diet, and how does it differ from other diets?
A: The GAPS diet, short for Gut and Psychology Syndrome diet, focuses on healing the gut lining by eliminating processed foods, sugars, grains, and introducing nutrient-dense, gut-friendly foods like bone broth, fermented vegetables, and healthy fats. Unlike many diets that prioritize weight loss or calorie counting, GAPS zeroes in on restoring digestive health and reducing inflammation from within.
Q2: How can the GAPS diet help alleviate chronic pain?
A: Chronic pain often stems from systemic inflammation and imbalances in the gut microbiome. By repairing the gut lining and reducing inflammatory triggers, the GAPS diet may decrease systemic inflammation, which in turn can lessen conditions like arthritis, migraines, and fibromyalgia. Essentially, healing the gut helps calm the body’s pain signals.
Q3: Is there scientific evidence supporting the GAPS diet’s effect on pain relief?
A: While anecdotal reports and case studies highlight impressive improvements in pain and inflammation, large-scale scientific studies on the GAPS diet are still limited. However, emerging research on gut health, inflammation, and chronic pain supports the principle that addressing gut integrity can influence pain perception.
Q4: What challenges might someone face when starting the GAPS diet?
A: Transitioning to the GAPS diet can be intense. Food restrictions are significant, which may lead to cravings and social difficulties. Some individuals experience “healing reactions” — temporary worsening of symptoms — as their gut microbiome shifts. Patience and careful planning are essential to successfully navigate these initial hurdles.
Q5: Can the GAPS diet be combined with other medical treatments for pain?
A: Absolutely. The GAPS diet complements medical care but should not replace prescribed treatments without professional guidance. Patients should consult healthcare providers to create a holistic pain management plan incorporating diet, medication, physical therapy, or other modalities as needed.
Q6: Who might benefit most from adopting the GAPS diet?
A: Individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions, digestive disorders, autoimmune diseases, or unexplained pain may find relief through the GAPS diet. It’s especially beneficial for those who suspect their pain is linked to gut health but should be personalized to each person’s needs.
Q7: What are some common success stories from people living pain-free on GAPS?
A: Many share stories of diminished joint pain, reduced migraine frequency, and newfound energy after months on GAPS. Reports often include improved mood and sleep, highlighting a broader sense of well-being beyond pain relief—proof that a healthy gut nurtures the whole body.
Q8: How can someone get started with the GAPS diet safely?
A: Starting the GAPS diet involves a careful step-by-step introduction of foods, beginning with the “Introduction Diet” phase. Working with a practitioner familiar with GAPS can help tailor the plan, monitor progress, and prevent nutritional gaps, helping individuals transition smoothly to a pain-free life.
To Wrap It Up
In the journey toward a life unburdened by pain, the GAPS diet offers more than just a nutritional plan—it presents a pathway to restoration and renewed vitality. By nurturing the gut and embracing wholesome, natural foods, many have discovered relief where conventional methods fell short. While individual experiences may vary, the promise of living pain-free through mindful eating invites us all to reconsider the profound connection between what we consume and how we feel. Embracing this lifestyle might just be the key to unlocking a quieter, more comfortable existence—one meal at a time.












Leave feedback about this